From IaaS to FaaS: A Deep Dive into Four Types of Cloud Services
enterprise cloud services
In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, businesses increasingly turn to cloud computing to streamline operations, enhance scalability, and boost overall efficiency. One of the key driving forces behind this transformation is adopting enterprise cloud services. These cloud services offer a wide range of solutions tailored to satisfy the various needs of businesses, helping them stay competitive in an ever-evolving market. This article will shed light on the four primary types of cloud services organizations leverage to thrive in the modern business environment.
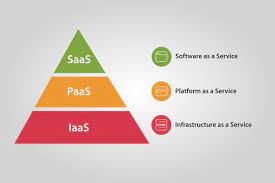
1. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Building Blocks for Enterprise IT
Infrastructure as a Service, commonly called IaaS, forms the foundation of cloud services. It provides businesses with essential computing resources over the Internet, including virtualized servers, storage, and networking components. IaaS allows organizations to avoid the costs and complexities associated with maintaining physical hardware and data centers. Instead, they can rent the infrastructure they need from cloud service providers on a pay-as-you-go basis.
One of the key benefits of IaaS is its scalability. Enterprises can easily adjust their resources to accommodate fluctuating workloads, ensuring optimal performance without overprovisioning. This flexibility is particularly valuable for companies with seasonal demand variations or rapidly evolving IT needs. Major cloud providers such as AWS-Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) offer robust IaaS solutions, empowering enterprises to build and manage their IT infrastructure efficiently.
2. Platform as a Service (PaaS): Streamlining Application Development
Platform as a Service, or PaaS, caters to the needs of enterprise developers and software engineers. It provides a comprehensive environment for building, deploying, and managing applications without the complexities of managing the underlying infrastructure. With PaaS, developers can focus on coding and innovation rather than the nuances of server maintenance and software updates.
PaaS provides a range of tools and services that streamline the development process. This includes database management, application hosting, and middleware services. PaaS solutions enable faster time-to-market for applications, enhance collaboration among development teams, and facilitate continuous integration and delivery (CI/CD) practices. Popular PaaS offerings include Microsoft Azure App Service, Google App Engine, and Heroku, making it easier for enterprises to create and deploy their applications.
3. Software as a Service (SaaS): On-Demand Applications for Enterprises
Software as a Service, or SaaS, represents one of the most recognizable forms of cloud services. It provides businesses access to a wide range of software applications hosted in the cloud and delivered over the Internet. This model eliminates the need for on-premises software installation and maintenance, simplifying the software lifecycle management for organizations.
Enterprise SaaS offerings cover a broad spectrum of applications, from customer relationship management (CRM) and enterprise resource planning (ERP) to productivity and collaboration tools. Prominent examples include Salesforce, Microsoft 365, and Zoom. SaaS solutions are highly scalable and customizable, allowing businesses to tailor their software stack to suit their unique requirements.
4. Function as a Service (FaaS): Enabling Serverless Computing
Function as a Service, or FaaS, is a cloud computing model where cloud service providers manage the infrastructure, automatically scaling resources to match the application’s workload. Developers write code in the form of small, independent functions that are executed in response to specific events or triggers without the need to provision or manage servers.
FaaS is gaining popularity in the enterprise sector due to its efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and agility. It allows organizations to focus solely on code development, as cloud providers handle all aspects of infrastructure management, including auto-scaling, load balancing, and security. AWS Lambda, Azure Functions, and Google Cloud Functions are leading FaaS platforms that offer seamless integration with other cloud services, enabling organizations to build sophisticated and highly responsive applications.
In conclusion, enterprise cloud services are pivotal in modernizing business operations, enhancing agility, and driving innovation. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), Software as a Service (SaaS), and Function as a Service (FaaS) are the four primary types of cloud services that cater to various aspects of organizational needs. By strategically leveraging these cloud computing models, enterprises can position themselves for success in today’s digital and competitive landscape.